描述
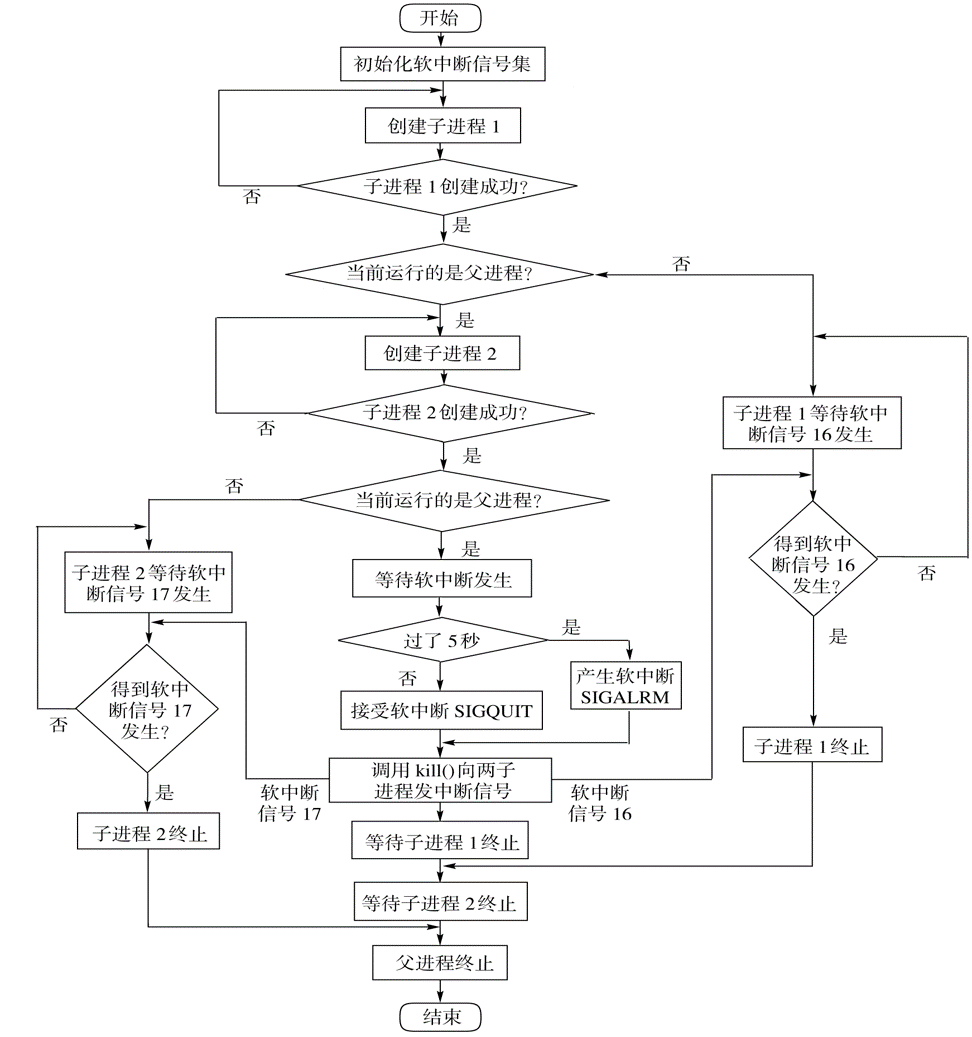
使用系统调用fork()创建两个子进程,再用系统调用signal()让父进程捕捉键盘上发出的中断信号(即按ctrl+c键),当父进程接收到这两个软中断的某一个后,父进程用系统调用kill()向两个子进程分别发出整数值为16和17软中断信号,子进程获得对应软中断信号,然后分别输出下列信息后终止:
流程图:
实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/wait.h> int wait_flag = 1 ;void stop1 () void stop2 () int main (int argc,char ** argv) pid_t pid1,pid2; signal(2 ,stop1); while ((pid1 = fork()) == -1 ); if (pid1 > 0 ) { while ((pid2 = fork()) == -1 ); if (pid2 > 0 ) { sleep(5 ); kill(pid1,16 ); wait(0 ); kill(pid2,17 ); wait(0 ); printf ("\nParent process is killed!\n" ); exit (0 ); } else { signal(17 ,stop2); while (wait_flag) ; printf ("\nChild process 2 is killed by parent!\n" ); exit (0 ); } } else { signal(16 ,stop2); while (wait_flag) ; printf ("\nChild process 1 is killed by parent!\n" ); exit (0 ); } } void stop1 () printf ("\nParent process catches the interruption signal!\n" ); } void stop2 () wait_flag = 0 ; printf ("\nChild process catches the interruption signal!\n" ); }
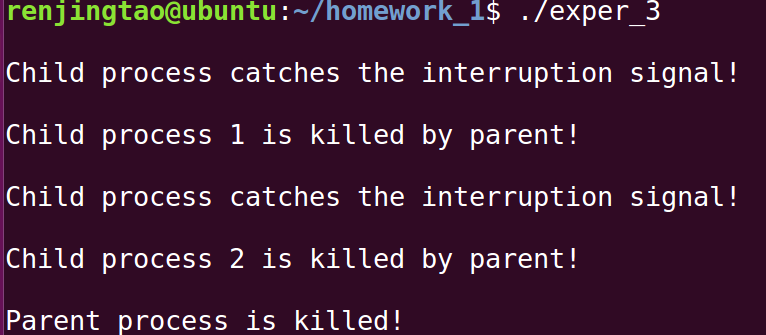
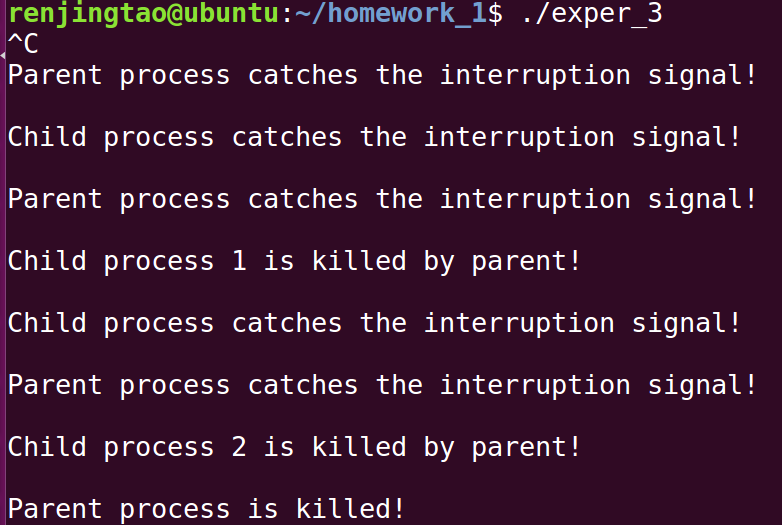
结果
5s内没有按终止键:
5s内按下ctrl+c:
附
系统调用signal(sig,function):捕捉中断信号sig后执行function规定的操作。int sig,void* func()